In the United States, colorectal cancer (CRC) stands as the second most common cause of cancer death. Despite its prevalence and the availability of effective screening methods, disparities persist in screening rates, particularly among Hispanic and Latino populations. Contrary to popular belief, AI can reduce disparities in healthcare and close care gaps among under-served populations. Our multilingual AI care agent demonstrated this potential by achieving FIT-test opt-in rates that were 2.6 times higher among Spanish-speaking patients compared to English-speaking patients. This innovative approach not only bridges language barriers but also addresses healthcare disparities, effectively closing care gaps for traditionally underserved Spanish-speaking communities.
The Importance of FIT Testing
Fecal immunochemical tests (FITs) have become crucial in colorectal cancer detection, boasting high accuracy and specificity. Despite widespread endorsement by major health organizations and comprehensive coverage under the Affordable Care Act, significant disparities exist in screening rates between Hispanic and Latino populations (53.4%) and non-Hispanic whites (70.4%)¹. These disparities are reflected in higher mortality rates from metastatic disease among Hispanics compared to non-Hispanic whites. Various barriers, including language, contribute to lower screening rates in Hispanic communities, which is where our AI-powered solution aims to make a difference.

Introducing Ana: AI-Powered Outreach for Colorectal Cancer Screening
In collaboration with WellSpan Health, a leading integrated health system serving central Pennsylvania and northern Maryland, we’ve launched an innovative AI platform to address the screening gap. Our AI agent, named Ana, is designed to conduct targeted outreach to at-risk patients, with a particular focus on Spanish-speaking populations. Ana’s capabilities go beyond simple automated messaging. She engages patients in natural, empathetic conversations, explains the importance of colorectal cancer screening, answers questions, and helps schedule FIT test kit deliveries. Because Ana is fluent in both English and Spanish, she can connect with patients in their preferred language
Our Intervention
In partnership with WellSpan Health, we aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of AI-powered outreach calls in improving colorectal cancer screening rates among Spanish-speaking patients compared to English-speaking patients. We analyzed data from 1,878 AI-powered outreach calls conducted from September 16 – 24, 2024, of which 517 (28%) were conducted in Spanish.
The calls were made to patients eligible for colorectal cancer screening, and our analysis looked at patients who’s date of birth was verified. Importantly, our outreach was specifically directed at patients, both English- and Spanish-speaking, who were not actively engaged with the healthcare system—those without online profiles and who were unlikely to be reached effectively through traditional methods like email. We looked at call engagement (connect rates and call durations) and FIT test kit opt-in rates.
Results
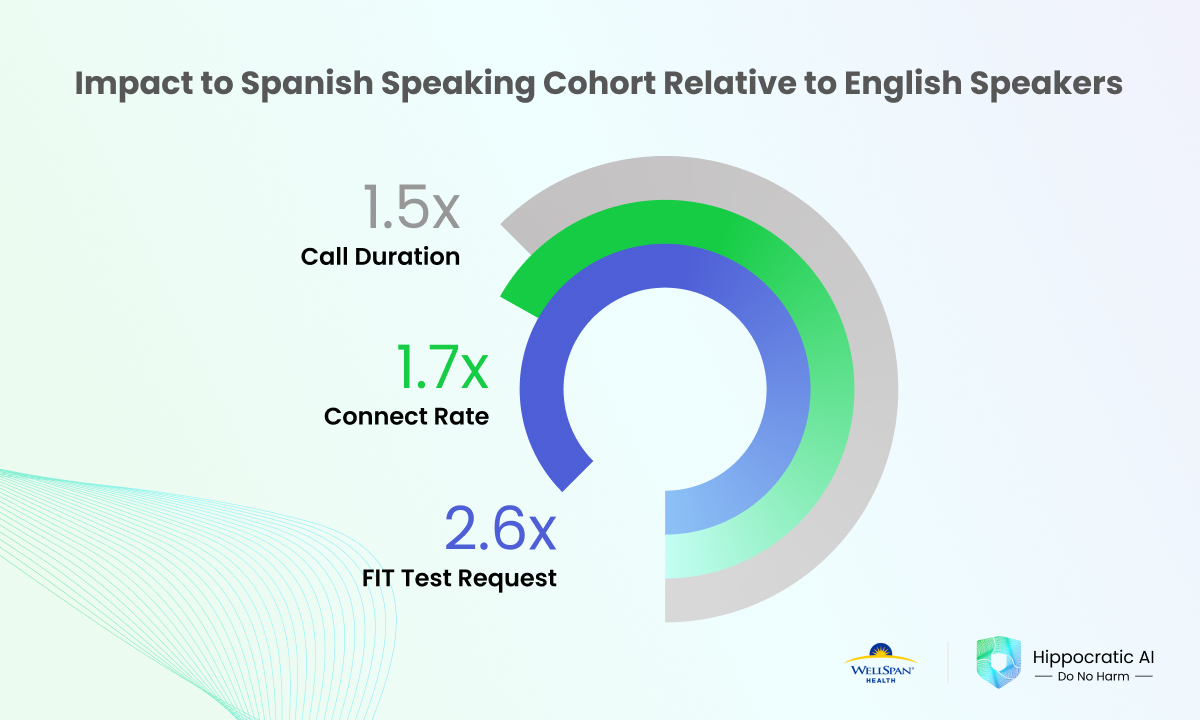
Our findings revealed striking differences in engagement and outcomes between Spanish-speaking and English-speaking patients:
1. Engagement. Spanish-speaking patients were significantly more engaged in outreach with the AI care agent than English-speaking patients:
-
Connect rate: 89% for Spanish-speaking vs. 53% for English-speaking patients (p < 0.0001)
-
Call duration: 6.05 minutes for Spanish-speaking vs. 4.03 minutes for English-speaking patients (p < 0.0001). This difference is primarily because Spanish speakers are less likely than English speakers to hang up in the first few minutes of the call.
2. Outcomes. Spanish-speaking patients were 2.6 times more likely to request FIT test screening kits compared to English-speaking patients:
-
18% for Spanish-speaking vs. 7% for English-speaking patients (p < 0.0001)
Spanish-speaking patients showed significantly higher responsiveness to AI-powered outreach compared to English-speaking patients on measures of engagement. Most notably, FIT test kit opt-in rates among Spanish-language patients were 2.6 times those of their English-language counterparts.

Bridging the Language Gap with AI
The success of our AI-powered outreach among Spanish-speaking patients highlights the potential of this technology to reduce long-standing healthcare disparities. By providing competent, language-specific outreach, we’ve been able to significantly improve engagement and increase the rates of people agreeing to be screened in a traditionally underserved population.
Several factors may contribute to the increased effectiveness of AI-powered outreach among Spanish-speaking patients:
Language Barrier Elimination: Ana’s ability to communicate fluently in Spanish removes a significant obstacle to healthcare access and understanding.
Convenience and Accessibility: Patients can engage with Ana from the comfort of their homes, at times that suit them best.
Removal of Time Constraints: Unlike human callers who may face time productivity targets, Ana can patiently answer questions and provide detailed explanations without rushing.
Moving Forward with AI Outreach to Close Care Gaps
Contrary to popular belief, AI has the potential to promote equity and close care gaps in healthcare. Our experience with Hippocratic AI’s care agents demonstrates the power of empathic, multilingual AI to overcome healthcare inequities in underserved populations. We invite healthcare system leaders and providers committed to health equity to explore these transformative capabilities.
Appendix
1. Viramontes O, Bastani R, Yang L, Glenn BA, Herrmann AK, May FP. Colorectal cancer screening among Hispanics in the United States: Disparities, modalities, predictors, and regional variation. Prev Med. 2020;138(106146):106146.